Physics for Class 10 Students
Electricity
IntroductionIn this article, you will be able to know and learn about some essential terminologies used in electricity. Electricity plays a vital role in doing our work. Commercially available electricity is a controllable and convenient form of energy for a variety of uses in homes, schools, hospitals, and industries. So in this lesson, we shall study the technological and scientific aspects of electricity along with the heating effect of electric current and its applications.
Some important terminologies used in the lesson on electricity are:
Ammeter
· Ammeter refers to an instrument that measures electric current in a circuit.
· Ammeter is always connected in series in a circuit through which the current is to be measured.
Conductor
Conductors refer to substances that allow electricity to pass through them easily.
· Drift speed refers to the average velocity of the free charges.
· Drift speed refers to the average speed at which electrons or ions progress through a medium.
· Drift speed or velocity is in the direction opposite to the electric field for electrons.
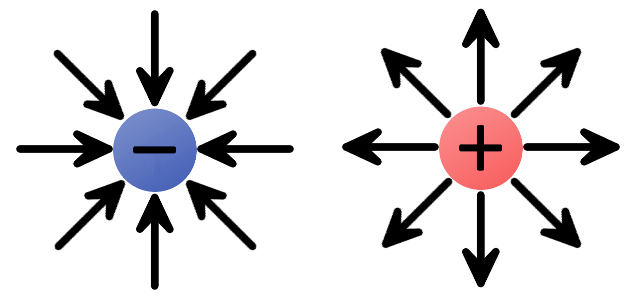
Electric charge
· Electric charge refers to the basic property of matter carried by some elementary particles that govern how the particles are affected by an electric or magnetic field.
· Electric charge can be positive or negative.
Electric circuit
Electric potential
· The electric potential or voltage refers to the difference in potential energy per unit charge between two locations in an electric field.
· Electric potential refers to the amount of work needed to move a unit charge from a reference point (earth) to a specific point against an electric field.
· Electric potential is the work done per unit charge in bringing the charge from infinity to that point against electrostatic force.
Electric power
· Electric power refers to the rate per unit time at which electrical energy is transferred by an electric circuit.
· Electric power refers to the rate of doing work by electricity.
Electrical energy
· Electrical energy refers to energy derived as a result of the movement of electrons.
· Electrical energy is a form of energy resulting from the flow of electric charge.
Electricity
· Electricity refers to the flow of electrical power or charge.
· Electricity is a secondary energy source.
· Lightning is an example of electricity.
Electron
· The electron is a subatomic particle whose electric charge is negative.
· Electrons are subatomic particles that hold an elementary charge of magnitude -1.
Free electrons
· Free electrons refer to the electrons which are not attached to the nucleus of an atom and are free to move when external energy is applied.
· Free electron is an electron moving in a vacuum.
· Free electrons are electrons present in the valence shell of an atom and are loosely bound to the atom's nucleus.
Fuse
· Fuse refers to an electrical safety device that provides overcurrent protection of an electrical circuit.
· Fuse is an electrical safety device that limits the current flowing in an electric circuit.
Heating effect of electric current
· When electric current flows through a conducting wire, the temperature of the wire increases.
· For example, a bulb becomes hot after its use for some time.
Insulator
· An electrical insulator is a material in which electric current does not flow freely.
· Insulator is a material that is a poor conductor of electricity and heat.
· An electrically insulating material is used for separating or supporting conductors.
Joule’s law of heating
Joule’s law of heating states that when a current ‘i’ passes through a conductor of resistance ‘r’ for time ‘t’ then the heat developed in the conductor is equal to the product of the square of the current, resistance, and time.
Negative charge
· Negative charge refers to an electrical property of a particle at the subatomic scale.
· In ordinary matter, negative charge is carried by electrons.
· An object is negatively charged if it has more electrons than protons.
Ohm’s law
· Ohm’s law states that the current flowing through a conductor is directly proportional to the potential difference applied across its ends, provided the temperature and other physical conditions remain unchanged.
· Ohm’s law is a formula used to calculate the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance in an electrical circuit.
One Ampere
One Ampere refers to the flow of one Coulomb of charge per second.
One Coulomb
One Coulomb is the charge flowing through a wire in one second(s) if the current is one Ampere.
One Ohm
· One Ohm refers to the resistance of a conductor with a potential difference of one volt applied to the ends through which one-ampere current flows.
· One Ohm is equal to the resistance of a conductor through which a current of one ampere flows when a potential difference of one volt is applied to it.
One Volt
A potential difference of one volt is equal to one joule of energy being used by one coulomb of charge when it flows between two points in a circuit.
One Watt
One watt refers to the power produced when 1 Joule of work is done for 1 second i.e. 1W=(1J)/(1s).
One Watt-hour
· One Watt-hour refers to the energy consumed when 1 watt of power is used for 1 hour.
· One Watt-hour is a unit of energy.
· One Watt-hour is a way to measure the amount of work performed or generated.
· One Watt-hour measures the amount of energy for a specific period of time.
Positive charge
· The matter is positively charged when the number of protons exceeds the number of electrons.
· A proton carries a positive charge in the nuclei of atoms.
· A positive charge can be created by adding protons to an atom or object with a neutral charge.
· A positive charge can also be created by removing electrons from a neutrally charged object.
Potential difference
· Potential difference is the difference in electrical potential between two points.
· Potential difference refers to the work done to move a unit charge from one point to another.
· Potential difference refers to the difference in the amount of energy that charge carriers have between two points in a circuit.
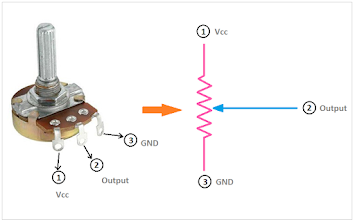
Potentiometer
· Potentiometer refers to a variable resistor used as a potential divider by using three terminals.
· Potentiometer is an instrument for measuring an electromotive force by balancing it against the potential difference produced by passing a known current through a known variable resistance.
Resistor
A resistor refers to a conductor having some appreciable resistance.Rheostat
Rheostat refers to a variable resistor using two terminals as a potential divider.Steady current
· Steady current is also known as constant current, time-independent current, and stationary current.
· A steady current refers to a type of direct current (DC) that does not change its intensity with time.
· In the case of steady current, the change in charge per unit time is constant.
Switch
· Switch refers to a device that is used to break an electric circuit.
· Switch refers to an electrical component that can disconnect or connect the conducting path in an electrical circuit, interrupting the electric current or diverting it from one conductor to another.
· Electric switch is a device used for opening and closing electrical circuits under normal load conditions, usually operated manually.
Variable resistance
Variable resistance refers to the component of an electric current that is used to regulate the current without changing the voltage from the source.Voltmeter· Voltmeter refers to an instrument used to measure the potential difference.
· The voltmeter is always connected in parallel across the points between which the potential difference is to be measured.
Wire
· A wire is a long thin piece of metal used to fasten things or carry electric current.
· A wire is a cable that carries power or signals from one place to another.
· A wire is a single cylindrical, flexible strand or rod of metal.
· Wires are used to bear mechanical loads or electricity and telecommunications signals.
Some SI units used in electricity are as follows:
1. Write the SI unit of electric charge.
The SI unit of electric charge is Coulomb.
2. Write the SI unit of electric current.
The SI unit of electric current is Ampere.
3. Write the SI unit of potential difference.
The SI unit of potential difference is volt or JC-1.
4. Write the SI unit of resistance.
The SI unit of resistance is the ohm.
5. Write the SI unit of resistivity.
The SI unit of resistivity is the Ohm meter.
6. Write the SI unit of electric power.
The SI unit of electric power is Watt.
7. Write the SI unit of the commercial unit of electric energy.
The SI unit of the commercial unit of electric energy is a Kilowatt hour (KWh).
To know more visit https://zueducator.blogspot.com


















No comments:
Post a Comment